ONLINE MEDICAL TRANSCRIPTION COURSE
Medical transcription as it is currently known has existed since the beginning of the 20th century when standardization of medical records and data became critical to research.At that time, medical stenographers recorded medical information, taking doctors' dictation in shorthand. With the creation of audio recording devices, it became possible for physicians and their transcribers to work asynchronously.
Over the years, transcription equipment has changed from manual typewriters, to electric typewriters, to word processors, and finally, as of 2021, to computers. Storage methods have also changed: from plastic disks and magnetic belts to cassettes, endless loops, and digital recordings. Today, speech recognition (SR), also known as continuous speech recognition (CSR), is increasingly used, with medical transcriptions and, in some cases, "editors" providing supplemental editorial services. Natural-language processing takes "automatic" transcription a step further, providing an interpretive function that speech recognition alone does not provide.
In the past, these medical reports consisted of very abbreviated handwritten notes that were added in the patient's file for interpretation by the primary physician responsible for the treatment. Ultimately, these handwritten notes and typed reports were consolidated into a single patient file and physically stored along with thousands of other patient records in the medical records department. Whenever the need arose to review the records of a specific patient, the patient's file would be retrieved from the filing cabinet and delivered to the requesting physician. To enhance this manual process, many medical record documents were produced in duplicate or triplicate by means of carbon copy.
In recent years,medical records have changed considerably. Although many physicians and hospitals still maintain paper records, the majority are stored as electronic records. This digital format allows for immediate remote access by any physician who is authorized to review the patient information. Reports are stored electronically and printed selectively as the need arises. Many healthcare providers today work using handheld PCs or personal data assistants (PDAs) and are now utilizing software on them to record dictation.
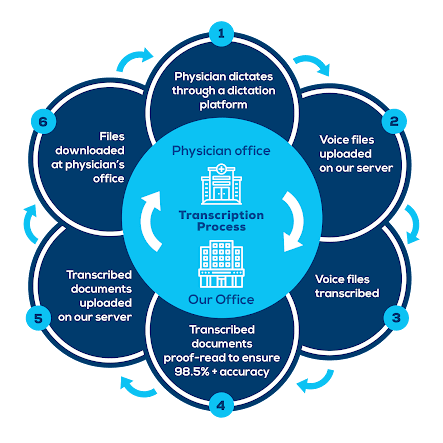
Medical transcription is part of the healthcare industry that renders and edits doctor dictated reports, procedures, and notes in an electronic format in order to create files representing the treatment history of patients. Health practitioners dictate what they have done after performing procedures on patients, and MTs transcribe the oral dictation, edit reports that have gone through speech recognition software, or both.
Pertinent, up-to-date and confidential patient information is converted to a written text document by a medical transcriptionist (MT). This text may be printed and placed in the patient's record, retained only in its electronic format, or placed in the patient's record and also retained in its electronic format. Medical transcription can be performed by MTs who are employees in a hospital or who work at home as telecommuting employees for the hospital; by MTs working as telecommuting employees or independent contractors for an outsourced service that performs the work offsite under contract to a hospital, clinic, physician group or other healthcare provider; or by MTs working directly for the providers of service (doctors or their group practices) either on-site or telecommuting as employees or contractors. Hospital facilities often prefer electronic storage of medical records due to the sheer volume of hospital patients and the accompanying paperwork. The electronic storage in their database gives immediate access to subsequent departments or providers regarding the patient's care to date, notation of previous or present medications, notification of allergies, and establishes a history on the patient to facilitate healthcare delivery regardless of geographical distance or location.
The term transcript, or "report" is used to refer to a healthcare professional's specific encounter with a patient. This report is also referred to by many as a "medical record". Each specific transcribed record or report, with its own specific date of service, is then merged and becomes part of the larger patient record commonly known as the patient's medical history. This record is often called the patient's "chart" in a hospital setting.
Medical transcription encompasses the medical transcriptionist, performing document typing and formatting functions according to an established criterion or format, transcribing the spoken word of the patient's care information into a written, easily readable form. A proper transcription requires correct spelling of all terms and words, and correcting medical terminology or dictation errors. Medical transcriptionists also edit the transcribed documents, print or return the completed documents in a timely fashion. All transcription reports must comply with medico-legal concerns, policies and procedures, and laws under patient confidentiality.
What Does a Medical Transcriptionist Do?
Doctors, nurse practitioners, and other healthcare providers dictate their confidential notes about each visit. Transcriptionists take these notes and transcribe them into a comprehensive record of the visit.
They use a template based on the type of practice, with most specialties having different requirements. Sometimes they receive files that are unedited speech-to-text translations. They then edit and format these notes and turn them into a finished document
While they are transcribing, medical transcriptionists use their extensive medical terminology knowledge and critical thinking skills to make sure mistakes are minimized. If they encounter conflicting information, such as a person listed as taking a medication that they are allergic to, they stop and get clarification to make sure the record is accurate.
Comments
Post a Comment